Question 1.
Newlands proposed the law of octaves. Mendeleeff suggested eight groups for elements in his table. How do you explain these observations in terms of modem periodic classification? (AS1)
(OR)
Correlate various tables proposed on classification of elements.
Answer:
- According to Newlands, every eighth element starting from a given element jsembles in its properties to that of the starting element, when elements are ranged in ascending order of their atomic weights.
- According to Newlands, the properties of fluorine and chlorine are similar and sodium and potassium are similar. Same aspect is given by modern periodic table.
- Mendeleeff divided it into horizontal rows and vertical columns. He called them peribds and groups respectively. Modem periodic table also gives the same.
- According to Mendeleeff, the elements of same group have similar properties. Modern periodic table also proposed the same thing.
- Mendeleeff gave the general formula for first group elements as R,0, and general formula for second group elements as RO. We can find the same thing in modern periodic table.
- The elements of particular group possess same common valency. Same was proposed by modern periodic table.
Question 2.
What are the limitations of Mendeleeff&rsquos periodic table? How could the modern periodic table overcome the limitations of Mendeleeff&rsquos table? (AS1)
(OR)
How can the limitations of Mendeleeffs table be overcome with the help of modern periodic table?
Answer:
Limitations of Mendeleeffs periodic table :
1) Anomalous pair of elements :
Certain elements of highest atomic weights precede those with lower atomic weights.
Eg : Tellurium (atomic weight 127.6) precedes iodine (atomic weight 126.9).
2) Dissimilar elements placed together :
a) Elements with dissimilar properties were placed in same group as sub-group A and sub-group Bt
Eg : Alkali metals like Li, Na, K, etc. of IA group have little resemblance with coinage metals like Cu, Ag, Au of IB group.
b) Cl of VII A group is a non-metal and Mn of VII B group is a metal.
Method of overcoming the limitations of Mendeleeffs periodic table by modern periodic table :
1. In modern periodic table, elements are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic numbers. So this arrangement eliminated the problem of anomalous series.
Eg : Though Tellurium (Te) has more atomic weight than Iodine (I), its atomic number is one unit less compared to Iodine.
2. The elements with similar outer shell (valence shell) electronic configurations in their atoms are in the same column called group in modern periodic table. So the elements have similar properties overcoming the Mendeleeffs second limitation.
Question 3.
Define the modern periodic law. Discuss the construction of the long form of the periodic table. (AS1)
(OR)
What are the salient features of modern periodic table?
Answer:
Modern periodic law :
&lsquoThe physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of the electronic configurations of their atoms&rdquo.
Construction of the long form periodic table :
- Based on the modern periodic law, the modern periodic table is proposed.
- This periodic table is known as long form of the periodic table.
- Long form periodic table is the graphical representation of Aufbau principle.
- The modern periodic table has 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows known as periods.
- There are 18 groups, represented by using Roman numerals I to VIII, with letters A and B in traditional notation, (or) 1 to 18 by Arabic numerals.
- There are 7 periods. These periods are represented by Arabic numerals 1 to 7.
- The number of main shells present in the atom of particular atom decides to which period it belongs.
- First period consists 2 elements, 2ndand 3rd periods contains 8 elements each, 4thand 5thperiods contains 18 elements each, 6 period contains 32 elements and 7thperiod is incomplete.
- The elements are classified into s, p, d and f block elements.
- Inert gases are placed in 18thgroup.
Question 4.
Explain how the elements are classified into s, p, d and f-block elements in the periodic table and give the advantage of this kind of classification. (AS1)
(OR)
How is the periodic table classified based upon the entering of differenciating electron? Explain that classification. What is the advantage of such classification?
Answer:
1) Depending upon which sub-shell the differentiating electron enters, the elements are classified into s, p, d and f-block elements. They are
- s - block elements,
- p - block elements,
- d - block elements,
- f - block elements.
2) s - block elements :
i) If the differentiating electron enters in s-sub-shell, then the elements are called s-block elements.
ii) IA (1), IIA (2) group elements belong to this block.
3) p - block elements :
i) If the differentiating electron enters in p-sub-shell, then the elements are called p-block elements.
ii) IIIA(13), IV A (14), V A (15), VIA (16), VIIA (17) belong to p-block.
4) d - block elements :
i) If the differentiating electron enters in d-sub-shell, then the elements are called d - block elements.
ii) I B, II B, III B, IV B, V B, VI B, VII B, VIII B belong to d-block elements.
iii) They are also called transition elements.
5) f - block elements :
i) If the differentiating electrons enter in f-sub-shell, then the elements are called f-block elements.
ii) These are divided into two types
a) Lanthanides (41 elements),
b) Actinides (5f elements).
iii) These are also called as inner transition elements.
Advantage of this classification :
1) The systematic grouping of elements into groups made the study simple.
2) Each period begins with the electron entering a new shell and ends with the complete filling of s and p-sub-shells of that shell.
Question 5.
Given below is the electronic configuration of elements A, B, C, D. (AS1)
| A) 1s2 2s2 |
1. Which are the elements coming within the same period? |
| B) 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 |
2. Which are the elements coming within the same group? |
| C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p³ |
3. Which are the noble gas elements? |
| D) 1s2 2s2 2p6 |
4. To which group and period does the element &lsquoC&rsquo belong? |
Answer:
According to electronic configuration
A = Be B = Mg C = P D = Ne
1. Which are the elements coming within the same period?
Answer:
A and D i.e. Be and Ne coming within the same period. [They have same valence shell (n = 2)]
2. Which are the ones coming within the same group?
Answer:
A and B i.e., Be and Mg coming within the same group. [They have same valence subshell with same valency (2s2 and 3s2)]
3. Which are the noble gas elements?
Answer:
D, i.e. Ne is the noble gas element. [It has valency as &lsquoO&rsquo and it has &lsquo8&rsquo electrons in valence shell].
4. To which group and period does the element &lsquoC&rsquo belong?
Answer:
Element &lsquoC&rsquo i.e. &lsquoP&rsquo belongs to 3rdperiod and VA group.
Question 6.
Write down the characteristics of the elements having atomic number 17. (AS1)
1) Electronic configuration ___________
2) Period number _____________
3) Group number _____________
4) Element family ____________
5) No. of valence electrons ___________
6) Valency _____________
7) Metal or non-metal ____________
Answer:
- 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p5
- 3
- VII A or 17
- Halogen family
- 7
- 1
- Non-metal
Question 7.
a) State the number of valence electrons, the group number and the period number of each element given in the following table : (AS1)

Answer:

b) State whether the following elements belong to a Group (G), Period (P) or neither Group nor Period (N). (AS1)

Answer:

Question 8.
Elements in a group generally possess similar properties, but elements along a period have different properties. How do you explain this statement? (AS1)
(OR)
Elements in a group possess similar properties, but elements along a period have different properties. Explain the reason.
Answer:
- Physical and chemical properties of elements are related to their electronic configurations, particularly the outer shell configurations.
- Therefore, all the elements in a group should have similar chemical properties.
- Similarly, across the table from left to right in any period, elements get an increase in the atomic number by one unit between any two successive elements.
- Therefore, the electronic configuration of valence shell of any two elements in a period is not same. Due to this reason, elements along a period possess different chemical properties.
Question 9.
s - block and p - block elements except 18thgroup elements are sometimes called as ‘Representative elements’ based on their abundant availability in the nature. Is it justified? Why? (AS1)
(OR)
Which elements are called representative elements? Why?
Answer:
- s, p - block elements are called representative elements because these are the elements which take part in chemical reactions because of incompletely filled outermost shell.
- These elements undergo chemical reactions to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration by losing or gaining or sharing of electrons.
- So they are called representative elements.
Question 10.
Complete the following table using periodic table. (AS1)

Answer:

Question 11.
Complete the following table using the periodic table. (AS1)
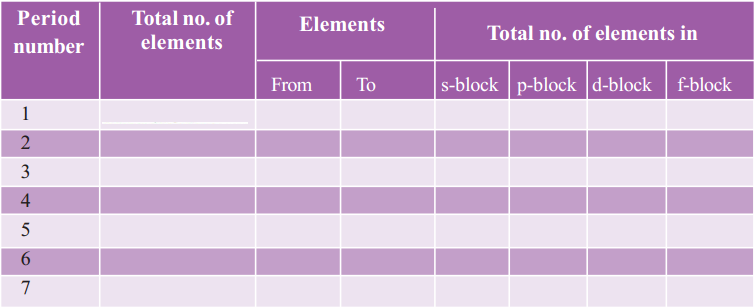
Answer:

Question 12.
The electronic configuration of the elements X, Y, and Z are given below.
a) X = 2
b) Y = 2, 6
c) Z = 2, 8, 2
i) Which element belongs to second period?
Answer:
Y belongs to second period.
ii) Which element belongs to second group?
Answer:
Z belongs to second group,
iii) Which element belongs to 18thgroup?
Answer:
X belongs to 18thgroup.
Question 13.
Identify the element that has the larger atomic radius in each pair of the following and mark it with a symbol (?). (AS1)
(i) Mg or Ca
(ii) Li or Cs
(iii) N or P
(iv) B or Al
Answer:

Question 14.
Identify the element that has the lower ionization energy in each pair of the, following and mark it with a symbol (?). (AS1)
(i) Mg or Na (ii) Li or O (iii) Br or F (iv) K or Br
Answer:

Question 15.
In period 2, element X is to the right of element Y. Then, find which ofitheydements have : (AS1)
i) Low nuclear charge
Answer:
Y has low nuclear charge.
ii) Low atomic size
Answer:
X has lower atomic size,
iii) High ionization energy
Answer:
X has higher ionization energy.
iv) High electronegativity
Answer:
Xhas high electronega^vity.
v) More metallic,character
Answer:
Y has more metallic character.
Question 16.
How does metallic character change when we move
i) Down a group?
ii) Across a period?
Answer:
i) Down a group :
When we move from top to bottom in a group, the metallic character increases.
ii) Across a period:
When we move left to right in a period, the metallic character decreases.
Question 17.
Why was the basis of classification of elements changed from the atomic mass to the atomic number? (AS1)
(OR)
Which atomic property is more suitable for classification of elements? Why?
Answer:
- The first attempt to classify elements was made by Dobereiner.
- Dobereiner’s attempt gave a clue that atomic masses could be correlated with properties of elements:
- Newlands’ law of octaves also followed the same basis for classification but this law is not valid for the elements that had atomic masses higher than calcium.
- Mendeleeff’s classification also based on the atomic masses of elements, but it lead to some limitations like Anomalous pair of elements and Dissimilar elements placed together.
- Moseley by analyzing the X-ray patterns of different elements was able to calculate the number of positive charges in the atoms of respective elements.
- With this analysis, Moseley realized that the atomic number is more fundamental
characteristic of an element than its atomic weight. ,
- So, he arranged the elements in the periodic table according to the increasing order of their atomic number.
- This arrangement eliminated the problem of anomalous series and dissimilar elements placed together in Mendeleeff’s classification.
Question 18.
What is a periodic property? How do the following properties change in a group and period? Explain. (AS1)
I. a) Atomic radius
b) Ionization energy
c) Electron affinity
d) Electronegativity
II. Explain the ionization energy order in the following sets of elements: (AS1)
a) Na, Al, Cl
b) Li, Be, B
c) C, N, O
d) F, Ne, Na
e) Be, Mg, Ca
Answer:
Periodic property:
The property in which there shall be a regular gradation is called periodic property.
I. a) Atomic radius :
Period :
Atomic radius of elements decreases across a period from left to right because the nuclear charge increases due to increase in atomic number.
Group :
Atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group due to addition of new shell.
b) Ionization energy:
Period :
When we move from left to right it does not follow a regular trend but generally increases due to increase in atomic number.
Group :
In a group from top to bottom, the ionization energy decreases due to increase in atomic size. -;
c) Electron affinity:
Period :
Electron affinity values increase from left to right in a period.
Group :
Electron affinity values decrease from top to bottom in a group.
d) Electronegativity :
Period :
Electronegativity increases from left to right in a period.
Group :
Electronegativity decreases from top to bottom in a group.
II. Ionization energy order :
a) Na, Al, Cl
b) Li, Be, B
c) C, N, O
d) F, Ne, Na
e) Be, Mg, Ca
Answer:
a) In a period ionisation energy increases so the order is Na < kl < Cl.
b) Beryllium has stable configuration 1s2 2s2. So it has more ionisation energy. So the order is Li < B < Be.
c) Nitrogen has half-filled p-orbitals. So it has greater ionisation energy. So the order is C < O < N.
d) Ne is inert gas right to F. Whereas Na is a metal ion in third period. So, the order is Na < F < Ne. e) In a group ionisation energy decreases. So the order is Be > Mg > Ca.
Question 19.
Name two elements that you would expect to have chemical properties similar to Mg. What is the basis for your choice? (AS2)
Answer:
- The two elements which have chemical properties similar to Magnesium are Beryllium and Calcium.
- The basis for my expectation is that they belong to same group as we know elements belonging to same group have similar properties.
Question 20.
On the basis of atomic numbers predict to which block the elements with atomic number 9, 37, 46 and 64 belong to? (AS2)
Answer:
- The element with atomic number 9 belongs to p-block.
- The element with atomic number 37 belongs to s-block.
- The element with atomic number 46 belongs to d-block.
- The element with atomic number 64 belongs to f-block.
Question 21.
Using the periodic table, predict the formula of compound formed between and element X of group 13 and another element Y of group 16. (AS2)
Answer:
The valency of 13thgroup elements is 3.
The valency of 16thgroup elements is 2.
The formula of compound is X2Y3.
Question 22.
An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 2 of the periodic table. State (AS2)
a) The no. of valence electrons
b) The valency.
c) Whether it is metal or a non-metal.
Answer:
a) The number of valence electrons are 2.
b) The valency of element is +2.
c) It is a metal.
Question 23.
An element has atomic number 19. Where would you expect this element in the periodic table and why? (AS2)
Answer:
The clement with atomic number 19 is in 4thperiod and first group of the periodic table.
Reason :
- Electronic configuration : 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p64s or [Ar]4s¹
- The differentiating electron enters into 4thshell. Hence it belongs to 4thperiod.
- The differentiating electron is in ‘s’ orbital. So it belongs to ‘s’ block.
- The outermost orbital has only one electron. Hence it belongs to first group.
Question 24.
Aluminium does not react with water at room temperature but reacts with both dil. HCl and NaOH solutions. Verify these statements experimentally. Write your observations with chemical equations. From these observations, can we conclude that Al is a metalloid? (AS3)
Answer:
- Aluminium reacts with dil. HCl and releases hydrogen gas with formation of Aluminium chloride.

Aluminium reacts with NaOH solution and releases hydrogen gas.

- The above two reactions says that Aluminium is amphoteric.
- Aluminium does not react with water at room temperature.
- This concludes that the properties of Aluminium are in between a metal and non¬metal. So it behaves like a metalloid.
Question 25.
Collect the information about reactivity of VIIIA group elements (noble gases) from internet or from your school library and prepare a report on their special character when compared to other elements of periodic table. (AS4)
Answer:
Reactivity of Noble gases :
- The noble gases show extremely low chemical reactivity.
- He and Ne do not form chemical compounds.
- Xenon, krypton and argon show only minor reactivity.
- The reactivity order follows like this : Ne < He < Ar < Kr < Xe < Rn.
- Xenon can form compounds like XeF2, XeF4and XeF6, etc.
Reasons for low reactivity :
- The extremely low reactivity of noble gases is due to stable electronic configuration.
- But as we move from top to bottom the reactivity increases. So xenon can form some compounds with high electronegative elements.
Question 26.
Collect information regarding metallic character of elements of IA group and prepare report to support the idea of metallic character increases in a group as we move from top ro bottom. (AS4)
Answer:
Metallic character of IA group elements :
- Alkali metals exhibit many of the physical properties common to metals but their densities are lower than those of other metals.
- Alkali metals have one electron in their outer shell which is loosely bound.
- They have largest atomic radii of the elements in their respective periods.
- The lower ionization energies result in their metallic properties and high reactivities.
- An alkali metal can easily lose its valence electron to form positive ion.
- So they have greater metallic character.
- The metallic character increases as we move from top to bottom in group due to addition of another shell, it is easy to lose electron.
Question 27.
How do you appreciate the role of electronic configuration of the atoms of elements in periodic classification? (AS6)
(OR)
How does electronic configuration help in the classification of elements in modern periodic table?
Answer:
The quantity is electronic configuration.
- Modern periodic table is based on electronic configuration. So elements are arranged in ascending order of their atomic numbers.
- The chemical properties of elements depend on valence electrons. The elements in same group have same number of valence electrons. So the elements belonging to same group have similar properties.
- So the construction of modern periodic table mainly depends on electronic configuration.
- Thus electronic configuration plays a major role in the preparation of modern periodic table. So its role is thoroughly appreciated.
Question 28.
Without knowing the electronic configurations of the atoms of elements Mendeleeff still could arrange the elements nearly close to the arrangements in the Modern periodic table. How can you appreciate this? (AS6)
Answer:
- Mendeleeff took consideration about chemical properties while arranging the elements. So the arrangement of elements is close to arrangement of elements in Modern periodic table.
- For this, he violated his periodic law.
- He left some gaps for elements, later those elements are discovered.
- So the efforts of Mendeleeff should be thoroughly appreciated.
Question 29.
Comment on the position of hydrogen in periodic table. (AS7)
Answer:
- Hydrogen is the element which has easier atomic structure than any other element.
- Electron configuration of hydrogen is Is1. It has one proton in its is nucleus and one electron in its is orbital.
- Hydrogen combines with halogens, oxygen and sulphur to form compounds having similar formulae just like alkali metals.
- Similarly, just like halogens, hydrogen also exists as diatomic molecule and combine with metals and non-metals to form covalent compounds.
- As alkali metals hydrogen can lose one electron and accept one electron as halogens.
- So in periodic table, its place may be in IA or VIIA group.
- But based on electronic configuration of hydrogen, it is placed in IA group.
Question 30.
How do the positions of elements in the periodic table help you to predict its chemical properties? Explain with an example. (As7)
Answer:
1) The physical and chemical properties of atoms of the elements depend on their electronic configuration, particularly the outer shell configurations.
2) Elements are placed in the periodic table according to the increasing order of their electronic configuration.
3) The elements in a group possess similar electronic configurations. Therefore all the elements in a group should have similar chemical properties.
Ex : Consider K
- It is the element in 4thperiod 1stgroup.
- Electron configuration : 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p64s¹.
- Differentiating electron enters into s-orbital. Hence it belongs to s-block.
- It is on the left side of the periodic table. Hence it is a metal.
- It is ready to lose one electron to get octet configuration. Hence its reactivity is more.
- It is Alkali metal.
- All alkali metals react with both acids and bases and releases H2gas.